Today’s hyper-connected world demands stable internet connectivity both for home and office. With the emergence of new technologies such as 5G and Wi-Fi 6, numerous individuals ask which one is apt for their requirements(5G vs Wi-Fi 6). Must you depend on Wi-Fi 6 exclusively for your office or home, or is 5G the ideal choice? Or maybe some of each is the best answer? Let’s analyze these two powerful technologies so that you can make an educated decision.
What Is 5G and Wi-Fi 6?
5G: The Next Generation of Cellular Connectivity
5G, the fifth generation of cellular technology, is the newest cellular evolution. In contrast to its predecessors, 5G delivers ultra-fast speeds, minimal latency, and huge numbers of devices connected over extensive areas.

It uses licensed spectrum bands and is controlled by telecom carriers, meaning a subscription plan is normally necessary.
Wi-Fi 6: The Future of Local Wireless Networks
Wi-Fi 6, or 802.11ax, is the latest wireless local area network (LAN) standard. Aimed at enhancing performance in the presence of numerous connected devices, Wi-Fi 6 features increased speed, increased efficiency, and enhanced capacity over earlier Wi-Fi standards.
Wi-Fi 6 works within unlicensed spectrum bands, so it is perfect for domestic and business use without the burden of ongoing service charges.

Key Differences Between 5G and Wi-Fi 6
| Feature | 5G | Wi-Fi 6 |
| Coverage | Wide-area (outdoor included) | Local area (indoor concentration) |
| Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 9.6 Gbps |
| Latency | <10 ms | <5 ms |
| Device Density | High (can support urban-scale deployment) | Optimized for high numbers of devices in close proximity |
| Use Cases | Mobile broadband, autonomous systems, outdoor remote work | Home/office Wi-Fi, IoT devices, gaming, video conferencing |
| Cost | Subscription-based | One-time equipment investment |
The variations highlight that although both technologies support high speeds and low latency, strengths are in different contexts.
Why Wi-Fi 6 Is Best for Home Use
For typical home consumers, Wi-Fi 6 is the way to go. Here’s why:
Fast Indoor Connection
Wi-Fi 6 ensures quick and reliable internet connectivity in and around the home, enabling applications such as streaming of 4K/8K videos, online gaming, and video calling. As more smart home products—such as smart TVs, security cameras, and voice assistants—are becoming ubiquitous, Wi-Fi 6 makes it possible for several devices to work in parallel without inhibiting the network.
Better Device Management
Wi-Fi 6 brings technologies like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Target Wake Time (TWT). These enable the router to handle many devices better, enhancing network performance in busy settings such as family houses with dozens of connected devices.

Cost-Effectiveness
In contrast to 5G, which has the need for a monthly carrier plan, Wi-Fi 6 has the added cost of an initial investment in compatible devices and a router. This is more cost-effective in the long term, particularly for domestic use where mobility is less crucial.
Wi-Fi 6E – The Next Step
Wi-Fi 6E takes Wi-Fi 6 to the 6 GHz band, with even less interference and more speed. If you require more performance for activities such as file transfers or video calls, moving to Wi-Fi 6E can give you future-proof speed.
The 5G Role in Office Usage
Office setups might not always be sufficient if you only depend on Wi-Fi 6. This is where 5G comes in to support your network configuration.
Seamless Mobility
For workers constantly on the move or traveling across big campuses, 5G offers campus-wide range and continuous connectivity. Compared to Wi-Fi, which often has limited range and needs to be reconnected manually every time it is moved between access points, 5G maintains devices connected as they move.
End-to-End Reliable Backup Connectivity
Adding a 5G link as a failover guarantees that business functions will not be disrupted in case of a disruption in Wi-Fi. Some newer routers blend Wi-Fi 6 and 5G capabilities, enabling offices to transition between the two seamlessly for uninterrupted internet connectivity.

Future-Ready Infrastructure
5G is not merely about speed—5G also enables new applications like edge computing, virtual reality (VR) conferencing, and Internet of Things (IoT) rollouts in industrial settings. For future-oriented companies, the inclusion of 5G in the lineup means that they are positioned for these new technologies.
When to Select 5G Over Wi-Fi 6
- Though Wi-Fi 6 provides most of the home and office use cases, there are certain use cases where 5G is the preferred choice:
- Remote Areas: Where fixed broadband infrastructure is not present, 5G provides high-speed internet without landline cables.
- Mobile Workers: Employees traveling frequently or those working from home can take advantage of 5G’s extensive coverage and steadfast connectivity.
- Outdoor Uses: 5G is perfect for outdoor applications such as autonomous cars, smart city uses, and outdoor surveillance systems.
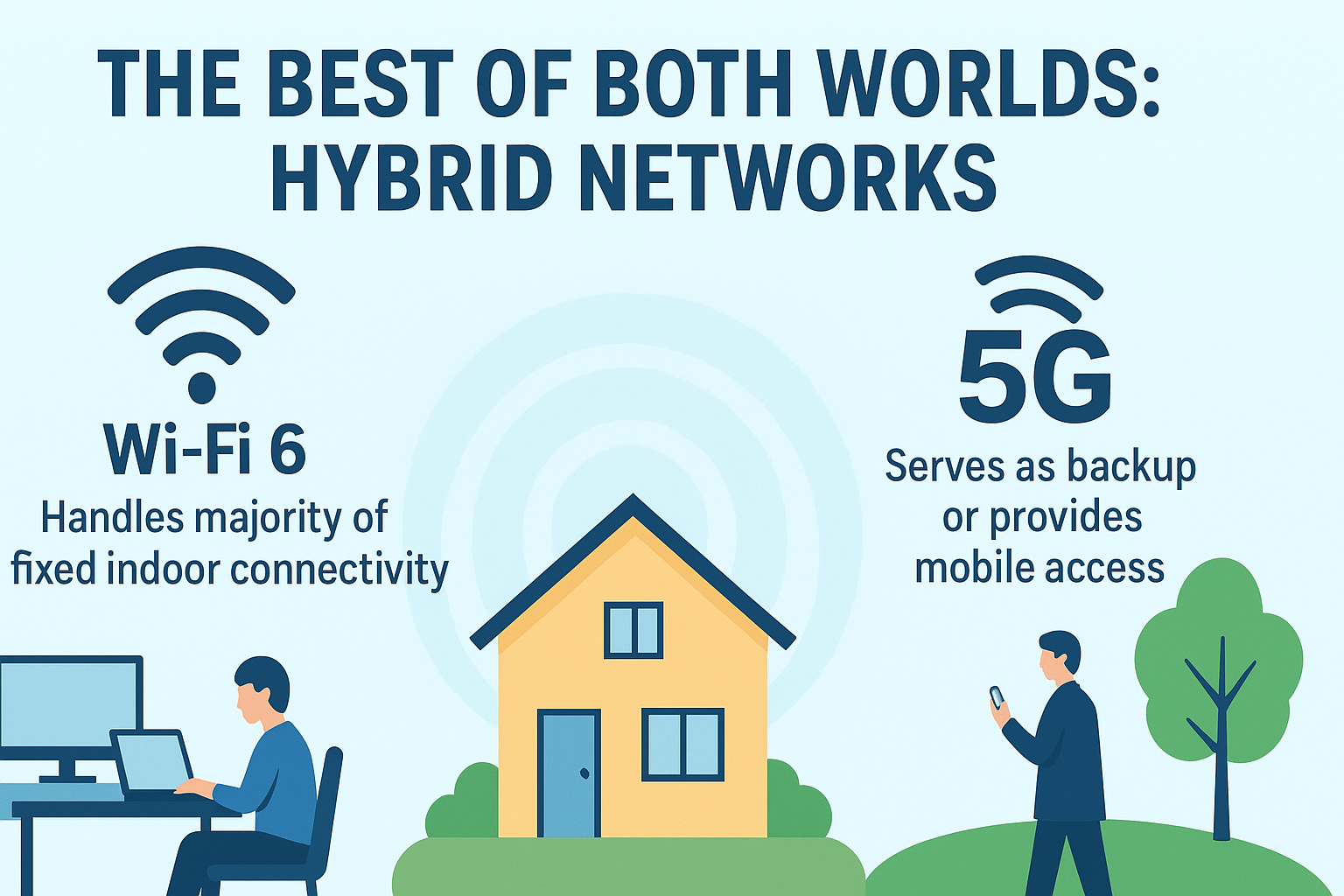
The Best of Both Worlds: Hybrid Networks
Rather than choosing one technology over the other, many homes and offices benefit from a hybrid approach:
- Wi-Fi 6 handles the majority of fixed indoor connectivity for devices like laptops, smart TVs, and desktops.
- 5G serves as a backup solution or provides mobile access for devices on the go or in outdoor areas.
This hybrid model ensures the highest possible uptime, better load management, and enhanced network flexibility.
Conclusion: What’s Best for You?
For most consumer home users, Wi-Fi 6 (or Wi-Fi 6E) is a cost-effective, high-speed solution. It can support multiple devices, deliver quick speeds, and doesn’t need continued service payments.
For office installations, the combination of Wi-Fi 6 and 5G provides the best of two worlds: secure, speedy local connections and convenient mobile internet access. Companies that seek smooth operations and future-proofed infrastructure should consider the integration of both technologies.
Lastly, 5G is priceless for remote and mobile applications, particularly when there is no wired broadband or when users require reliable connectivity over extensive areas.
By knowing your exact needs, usage habits, and budget, you can create a reliable network that takes advantage of the strengths of both 5G and Wi-Fi 6. More often than not, the best approach is not to choose between one and the other but to use both for maximum performance.










